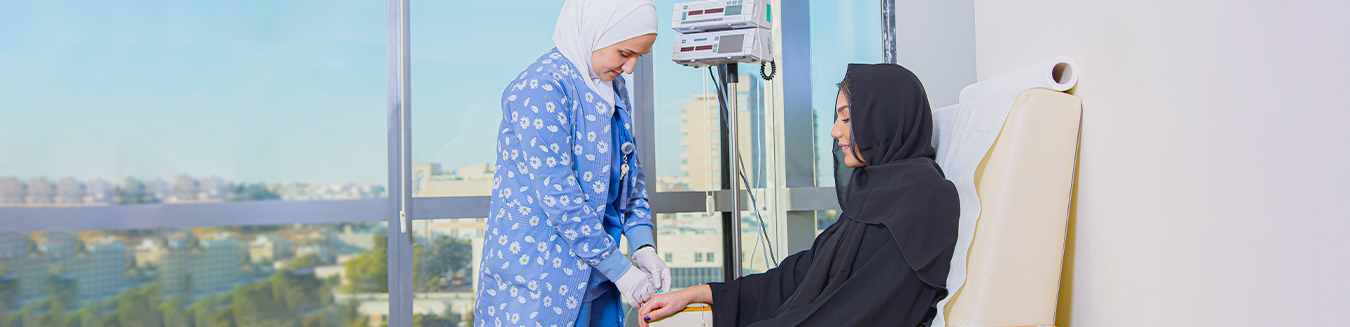
Chemotherapy is medicine given to cancer patients that is designed to kill cancer cells in the body. While it is a common type of cancer treatment, not all cancer patients require chemotherapy as a form of treatment.
How is chemotherapy administered?

Tablet Form

Intravenous Injection

Intramuscular Injection

Subcutaneous Injection
The side effects of chemotherapy
Chemotherapy works by targeting and eradicating rapidly growing and multiplying cancer cells. However, there are other healthy cells in the body that divide rapidly, which can be affected by chemotherapy, including hair cells.
Each chemotherapy drug can cause different side effects, yet they are usually temporary and end upon the conclusion of chemotherapy.
Common side effects
- Fatigue and lowered immunity (increasing the chance of infection) due to adverse effects in the bone marrow/blood cells.
- Hair loss.
- Nausea and vomiting, constipation and stomach pain.
- Loss of sexual drive and male infertility.
- Anemia.
- Weight gain or weight loss.
- Increased chance of bleeding and bruising.
General advice during chemotherapy
- Eat a variety of foods, especially those containing protein, which helps the body repair tissue that was damaged
- uring treatment.
- Avoid dairy products if you have diarrhea.
- Eat smaller meals to accommodate a loss of appetite.
- Always keep a bottle of water and snacks with you.
- Eat your favorite foods as your sense of taste may be temporarily affected.
- Avoid high-fat foods as they cause a feeling of fullness without providing enough nutrients.
- Do soft exercises like yoga and meditation to help uplift your spirits.