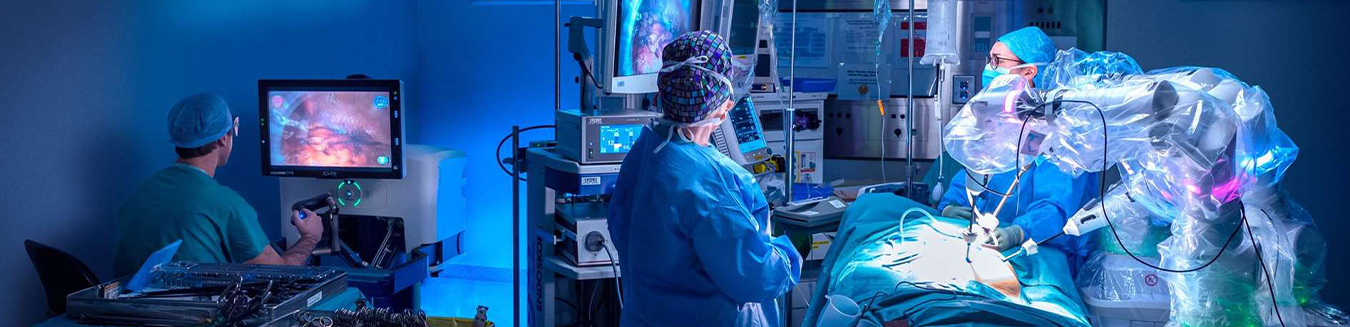
What is a Robotic Surgery System?
- It is one of the latest surgical systems used in medicine. It allows surgeons to perform complex surgeries with enhanced control, accuracy, and flexibility.
- The system relies on the use of a robot with three or four robotic arms to perform surgical procedures through direct control from the surgeon.
- The arms work simultaneously, where one is equipped with a camera, while two other arms act as the surgeon’s hands. The last arm is dedicated for assistance.
- The surgeon remains in control of the surgery through a control system that he guides using his hands and feet. Precise instruments are attached to the robotic arms, allowing the robotic arms to operate even through the tiniest of incisions.
- The surgeon operates a keyboard connected to a computer in the operating room, the computer is in turn connected to the robotic arms, where they are directed to the desired area in the surgery. Their position is very precisely determinable.
- Robotic surgery cannot replace a human surgeon. Rather, it is a way to enhance the surgeon’s skills and precision.
- The camera provides highly enlarged images on a high-resolution screen, with 3D images that are much more detailed compared to the naked eye.
Main Advantages of Robotic Surgery
- Minimally invasive surgery: Robotic surgery uses very fine instruments, allowing for very small surgical incisions, reaching less than 1 cm incisions in most cases.
- Control, precision, and flexibility: The use of surgical robots allows surgeons to perform complex surgeries with greater control, precision and flexibility compared to conventional surgery.
Benefitting Patients
- Robotic surgery can be used in many major surgeries, such as the surgical removal of cancerous tumors in the prostate, kidney, liver, uterus, colon and pancreas.
- Patients who may undergo this type of surgery will be selected based on:
- The joint decision of a multidisciplinary committee.
- Specific criteria that are applied separately for each specific case.
Results
- Faster post-surgery recovery:
- The minimal invasiveness nature of the surgery helps the body recover faster and with quick healing, small scars.
- Reducing patient’s stay after the medical procedure.
- Less Pain: Small incisions mean minimizing the pain and discomfort associated with the surgery.
- Reduced blood loss: The patient loses less blood during the surgery.
- Reduced wound complications.
- Reduced surgery waiting times: Allows surgeons as many surgical operations per day as possible, which is a much higher number when compared to traditional surgery.